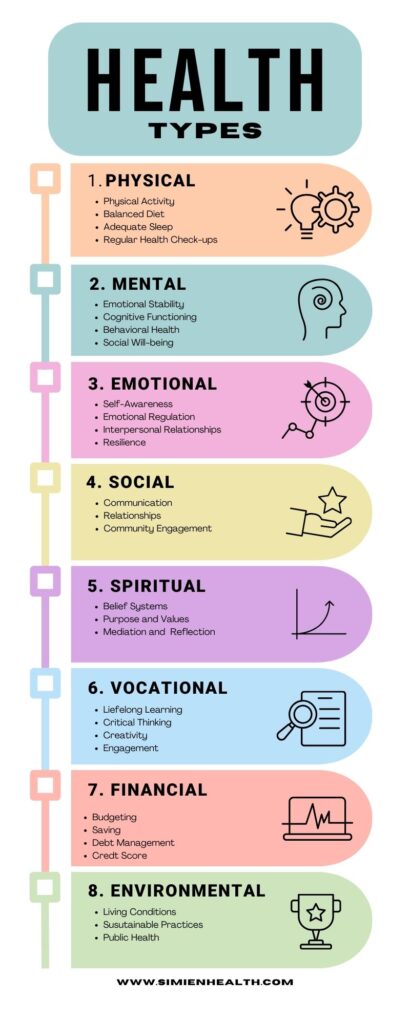
Understanding the Types of Health
Health Living is a multidimensional concept that extends beyond the absence of disease or infirmity. It encompasses various aspects of human life, each contributing to overall well-being. Understanding the different types of health is crucial for holistic well-being. This article explores the primary types of health and their importance in our daily lives.
1. Intro to Physical Health
Physical health refers to the well-being of the body and its optimal functioning. It encompasses a range of activities and lifestyle choices that contribute to the efficient operation of bodily systems and overall health. Physical health is crucial because it impacts every aspect of life, from basic daily activities to long-term wellness.
Key Features of Physical Health
a. Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is one of the most critical components of physical health. This includes exercises such as walking, running, cycling, swimming, and strength training. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity physical activity per week for adults.

b. Balanced Diet
A nutritious and balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients for the body to function correctly. This involves consuming a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, while limiting the intake of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats.
c. Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is vital for physical health. Adults typically need 7-9 hours of sleep per night to allow the body to repair and regenerate. Sleep plays a crucial role in immune function, metabolism, memory, learning, and other vital functions.

d. Regular Health Check-Ups
Routine health check-ups and screenings help in early detection and prevention of diseases. Regular visits to healthcare professionals for physical exams, vaccinations, and health screenings are essential components of maintaining physical health.

e. Proper Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is crucial for overall health. Water is necessary for digestion, nutrient absorption, temperature regulation, and joint lubrication. It’s recommended to drink at least 8 glasses (about 2 liters) of water a day.
f. Stress Management
Managing stress effectively is an important aspect of physical health. Chronic stress can lead to various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, depression, and weakened immune function. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and hobbies can help manage stress levels.

Benefits of Physical Health
a. Improved Cardiovascular Health
Engaging in regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, improves blood circulation, and reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. Exercise helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels and improves cholesterol profiles.

b. Enhanced Muscular and Skeletal Strength
Regular exercise, especially strength training, increases muscle mass, bone density, and joint flexibility. This reduces the risk of osteoporosis, fractures, and joint problems, particularly in older adults.
c. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is a significant benefit of regular physical activity and a balanced diet. It helps prevent obesity, which is a risk factor for many chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers.
d. Improved Mental Health
Physical health has a profound impact on mental well-being. Regular physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. It reduces symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress, and enhances cognitive function and self-esteem.
e. Enhanced Immune Function
Good physical health boosts the immune system, making the body more efficient at fighting off infections and diseases. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and a healthy diet contribute to a stronger immune response.
f. Increased Longevity
Healthy lifestyle choices that promote physical health are linked to increased life expectancy. Regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption contribute to a longer, healthier life.
g. Better Quality of Life
Overall, good physical health enhances the quality of life. It allows individuals to perform daily activities with ease, engage in recreational and social activities, and experience a greater sense of well-being and satisfaction.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Physical Health
a. Set Realistic Goals
Setting achievable health and fitness goals helps in maintaining motivation and tracking progress. Start with small, manageable changes and gradually increase the intensity and duration of physical activities.
b. Create a Balanced Routine
Incorporate a mix of cardiovascular, strength, flexibility, and balance exercises into your routine. This ensures comprehensive fitness and prevents monotony, keeping you engaged and motivated.
c. Stay Consistent
Consistency is key to achieving and maintaining physical health. Make physical activity a regular part of your daily routine, whether it’s a morning jog, a gym session, or an evening walk.
d. Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to your body’s signals. Rest when needed, and avoid pushing through pain or discomfort that could lead to injury. Proper recovery is essential for long-term health and performance.
e. Seek Professional Guidance
Consult healthcare professionals, nutritionists, or personal trainers for personalized advice and support. They can provide tailored guidance based on your individual health status and fitness goal.

Thoughts
Physical health is a foundational aspect of overall well-being. By incorporating regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, ensuring adequate sleep, staying hydrated, managing stress, and seeking regular health check-ups, individuals can significantly enhance their physical health. The benefits of such practices extend beyond the physical realm, contributing to improved mental health, increased longevity, and a better quality of life.

2. Mental Health
Mental health is as crucial as physical health and involves emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act. Key components include:
- Emotional Stability: Managing stress and emotions effectively.
- Cognitive Functioning: Maintaining clear thinking and memory.
- Behavioral Health: Adopting healthy coping mechanisms and behaviors.

Intro to Mental Health
Mental health encompasses our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how we think, feel, and act, and it helps determine how we handle stress, relate to others, and make choices. Mental health is important at every stage of life, from childhood and adolescence through adulthood.
Key Features of Mental Health
a. Emotional Well-being
Emotional well-being involves having positive emotions such as happiness, love, and satisfaction, and the ability to manage negative emotions like anger, sadness, and anxiety. It also includes resilience, or the ability to bounce back from difficult situations.
b. Psychological Well-being
Psychological well-being encompasses cognitive functioning and mental processes, including perception, memory, and thinking. It also involves having a sense of purpose and meaning in life, and the ability to manage stress effectively.
c. Social Well-being
Social well-being refers to the quality of relationships and interactions with others. It includes having supportive social networks, effective communication skills, and the ability to form and maintain healthy relationships.

d. Self-efficacy
Self-efficacy is the belief in one’s ability to succeed in specific situations or accomplish tasks. High self-efficacy can boost motivation and resilience, helping individuals to overcome challenges and achieve their goals.
e. Autonomy
Autonomy involves having control over one’s life and making independent decisions. It is essential for personal growth and self-determination, and it contributes to overall mental health.
f. Competence
Competence is the ability to effectively perform tasks and handle life’s demands. It includes skills, knowledge, and attitudes that enable individuals to function successfully in various areas of life.
You May Also Enjoy Reading “In-Depth Review of the Premium Curve Manual Treadmill SF-X7100: Performance and Value”
Benefits of Good Mental Health
a. Enhanced Quality of Life
Good mental health significantly enhances the quality of life. It enables individuals to enjoy life, pursue their interests, and achieve personal goals. People with good mental health tend to experience greater life satisfaction and well-being.
b. Better Physical Health
Mental and physical health are closely connected. Good mental health can improve physical health by reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. It can also boost the immune system and promote faster recovery from illnesses.

c. Improved Relationships
Healthy mental functioning fosters better relationships. Individuals with good mental health are better equipped to communicate effectively, resolve conflicts, and form strong, supportive connections with others.
d. Increased Productivity
Good mental health enhances productivity and performance in various aspects of life, including work, school, and personal projects. It enables individuals to focus, make decisions, and manage time efficiently.
e. Stress Management
Effective stress management is a significant benefit of good mental health. It involves recognizing and addressing stressors, using coping strategies, and maintaining a balanced lifestyle. This helps prevent stress-related disorders and improves overall resilience.
f. Emotional Stability
Good mental health provides emotional stability, allowing individuals to manage their emotions constructively. It reduces the impact of negative emotions and promotes positive emotional experiences, leading to greater happiness and contentment.
g. Increased Resilience
Resilience is the ability to adapt and recover from adversity. Good mental health enhances resilience, enabling individuals to cope with life’s challenges, setbacks, and traumatic events more effectively.
Strategies for Maintaining Mental Health
a. Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity can improve mental health by reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety, boosting mood, and enhancing overall well-being. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters.
b. Balanced Diet
A balanced diet supports mental health by providing essential nutrients for brain function. Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can improve mood, energy levels, and cognitive function.

c. Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is crucial for mental health. Adults typically need 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Adequate sleep improves mood, cognitive performance, and emotional regulation, and it reduces the risk of mental health disorders.
d. Mindfulness and Meditation
Practicing mindfulness and meditation can enhance mental health by reducing stress, improving focus, and promoting emotional regulation. These practices help individuals stay present and develop a deeper awareness of their thoughts and feelings.
e. Social Connections
Maintaining strong social connections is vital for mental health. Building and nurturing supportive relationships with family, friends, and community members provides emotional support, reduces feelings of loneliness, and enhances well-being.
f. Professional Help
Seeking professional help when needed is crucial for maintaining mental health. Therapists, counselors, and psychiatrists can provide support, guidance, and treatment for mental health issues, helping individuals to manage symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Thoughts
Mental health is a vital aspect of overall well-being, influencing how we think, feel, and act. By focusing on emotional, psychological, and social well-being, individuals can enhance their quality of life, improve physical health, foster better relationships, increase productivity, manage stress, achieve emotional stability, and build resilience. Adopting healthy lifestyle practices, such as regular physical activity, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, mindfulness, social connections, and seeking professional help when needed, can significantly contribute to good mental health.
3. Emotional Health
Emotional health focuses on how well we understand and manage our emotions. It includes:
- Self-Awareness: Recognizing and understanding one’s emotions.
- Emotional Regulation: Effectively managing and responding to emotional experiences.
- Interpersonal Relationships: Building healthy relationships with others.
Intro to Emotional Health
Emotional health, often interchanged with mental health, refers to the state of one’s emotions and the ability to manage and express them effectively. It encompasses emotional regulation, self-awareness, resilience, and the capacity to handle stress, build relationships, and recover from setbacks. Emotional health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, influencing both mental and physical health.
Key Features of Emotional Health
a. Emotional Awareness
Emotional awareness involves recognizing and understanding one’s emotions and their impact on thoughts and behaviors. This self-awareness helps in identifying emotions accurately and responding to them appropriately.
b. Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation is the ability to manage and control emotional reactions. This involves strategies to reduce negative emotions like anger or sadness and enhance positive emotions like joy and contentment.
c. Resilience
Resilience is the capacity to bounce back from adversity, trauma, or significant stress. It involves maintaining a positive outlook, coping with challenges, and adapting to change without prolonged periods of emotional distress.
d. Empathy
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. It is crucial for building and maintaining healthy relationships, fostering compassion, and creating strong social connections.
e. Stress Management
Effective stress management involves recognizing stressors and implementing techniques to reduce their impact. Strategies may include mindfulness, relaxation exercises, time management, and seeking social support.

f. Positive Relationships
Building and maintaining positive relationships are essential for emotional health. Healthy relationships provide support, increase feelings of belonging, and enhance life satisfaction.
g. Self-Esteem
Self-esteem refers to one’s overall sense of self-worth or personal value. High self-esteem contributes to emotional stability and confidence, while low self-esteem can lead to emotional distress and mental health issues.
Benefits of Emotional Health
a. Improved Mental Health
Good emotional health reduces the risk of mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and stress-related conditions. It promotes a positive mindset and emotional stability.
b. Enhanced Physical Health
Emotional health positively affects physical health. Managing stress and maintaining emotional balance can lower the risk of chronic diseases, improve immune function, and contribute to overall physical well-being.
c. Better Relationships
Emotional health fosters healthy, supportive relationships. It enhances communication skills, empathy, and the ability to resolve conflicts, leading to stronger personal and professional connections.

d. Increased Resilience
Emotionally healthy individuals are more resilient. They can cope with life’s challenges, recover from setbacks, and maintain a positive outlook even in difficult situations.
e. Greater Life Satisfaction
Good emotional health leads to greater life satisfaction and overall happiness. It enables individuals to enjoy life, engage in meaningful activities, and experience positive emotions more frequently.
f. Enhanced Productivity
Emotional health improves focus, motivation, and productivity. Emotionally balanced individuals are better able to manage their time, set and achieve goals, and perform effectively in various aspects of life.
g. Effective Stress Management
Emotional health equips individuals with strategies to manage stress effectively. This reduces the impact of stress on physical and mental health and enhances overall well-being.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Emotional Health
a. Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness involves being present in the moment and aware of thoughts and feelings without judgment. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help improve emotional regulation and reduce stress.
b. Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Healthy coping mechanisms include engaging in hobbies, physical activities, or creative pursuits that bring joy and relaxation. Avoiding unhealthy habits such as excessive drinking or drug use is crucial for emotional health.
c. Build a Support Network
Cultivating a support network of friends, family, and professionals provides emotional support and reduces feelings of isolation. Engaging in social activities and seeking help when needed are essential for emotional well-being.
d. Set Realistic Goals
Setting achievable and realistic goals enhances self-esteem and provides a sense of purpose. Breaking down larger goals into manageable steps can reduce feelings of overwhelm and increase motivation.
e. Seek Professional Help
When needed, seeking professional help from therapists, counselors, or support groups is crucial. Professional guidance can provide strategies for managing emotions and improving mental health.
f. Practice Gratitude
Regularly practicing gratitude by acknowledging and appreciating the positive aspects of life can improve emotional health. Keeping a gratitude journal or expressing thanks to others fosters a positive outlook.
g. Maintain Physical Health
Physical health and emotional health are interconnected. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and avoiding harmful substances contribute to better emotional well-being.
Thoughts
Emotional health is a fundamental component of overall well-being. It involves the ability to understand and manage emotions, build positive relationships, and cope with life’s challenges. The benefits of good emotional health extend to improved mental and physical health, better relationships, increased resilience, and greater life satisfaction. By practicing mindfulness, developing healthy coping mechanisms, building a support network, setting realistic goals, seeking professional help, practicing gratitude, and maintaining physical health, individuals can significantly enhance their emotional well-being.
4. Social Health
Social health pertains to our ability to form satisfying interpersonal relationships and adapt to social situations. It involves:
- Communication Skills: Effectively conveying and receiving messages.
- Relationships: Maintaining supportive and fulfilling connections with others.
- Community Engagement: Participating in community activities and feeling a sense of belonging.
Intro to Social Health
Social health refers to the ability of individuals to form healthy and rewarding relationships with others and to interact positively within the community. It encompasses various aspects of interpersonal relationships, community involvement, and social networks. Social health is a crucial component of overall well-being as it influences mental and physical health, providing support systems and a sense of belonging.
Key Features of Social Health
a. Positive Relationships
Developing and maintaining positive relationships with family, friends, and colleagues is fundamental to social health. Healthy relationships are characterized by mutual respect, trust, communication, and emotional support. These relationships provide a sense of security and belonging.
b. Effective Communication
Effective communication involves expressing oneself clearly and listening actively to others. It includes verbal and non-verbal communication skills, such as body language, eye contact, and tone of voice. Good communicators can resolve conflicts, express their needs, and build stronger connections with others.
c. Social Support Networks
Having a robust social support network is essential for social health. This network can include family members, friends, mentors, and community resources. Social support provides emotional comfort, practical assistance, and a buffer against stress and adversity.

d. Community Engagement
Active participation in community activities and events fosters social health. Volunteering, joining clubs or groups, and participating in local initiatives help individuals connect with others, build a sense of community, and contribute to the well-being of society.
e. Adaptability in Social Situations
Socially healthy individuals can adapt to different social situations and environments. They can navigate various social settings, form new relationships, and adjust to changes in their social lives. Adaptability enhances social interactions and resilience.
f. Empathy and Compassion
Empathy and compassion are crucial traits for social health. Empathy involves understanding and sharing the feelings of others, while compassion is the desire to help alleviate others’ suffering. These traits foster deeper connections and promote prosocial behavior.
Benefits of Social Health
a. Improved Mental Health
Strong social connections and support networks are linked to better mental health outcomes. Socially healthy individuals are less likely to experience depression, anxiety, and stress. Positive relationships provide emotional support and help individuals cope with challenges.
b. Enhanced Physical Health
Social health has a direct impact on physical health. Studies have shown that individuals with strong social ties have lower risks of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and diabetes. Social support can encourage healthy behaviors, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet.

c. Increased Longevity
Socially healthy individuals tend to live longer. Social connections and community involvement contribute to a higher quality of life and increased life expectancy. Social engagement promotes mental and physical well-being, which are crucial for longevity.
d. Better Coping Mechanisms
Social support provides individuals with better coping mechanisms during times of stress and adversity. Having people to turn to for advice, encouragement, and practical help can reduce the impact of stressful events and improve resilience.
e. Enhanced Self-Esteem and Confidence
Positive social interactions and relationships boost self-esteem and confidence. Feeling valued and supported by others enhances self-worth and contributes to a positive self-image. This, in turn, encourages individuals to pursue their goals and aspirations.
f. Greater Sense of Belonging
Social health fosters a sense of belonging and community. Being part of social networks and community activities provides individuals with a feeling of inclusion and purpose. This sense of belonging is essential for overall happiness and life satisfaction.
g. Reduced Risk of Isolation
Socially healthy individuals are less likely to experience social isolation and loneliness. Social isolation can have detrimental effects on mental and physical health. Maintaining social connections helps prevent feelings of loneliness and promotes overall well-being.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Social Health
a. Nurture Relationships
Invest time and effort in nurturing relationships with family, friends, and colleagues. Regular communication, spending quality time together, and showing appreciation and support can strengthen these bonds.
b. Improve Communication Skills
Work on improving communication skills by practicing active listening, being mindful of body language, and expressing thoughts and feelings clearly. Effective communication enhances relationships and helps resolve conflicts.
c. Join Social Groups or Clubs
Participate in social groups or clubs that align with your interests and hobbies. This provides opportunities to meet new people, build friendships, and engage in enjoyable activities.

d. Volunteer and Give Back
Engage in volunteer work and community service. Volunteering not only helps others but also fosters a sense of purpose and connection. It allows individuals to contribute to the well-being of their community.
e. Seek Support When Needed
Don’t hesitate to seek support when needed. Reach out to friends, family, or professionals for help during challenging times. Building a reliable support network is crucial for social health.
f. Practice Empathy and Compassion
Cultivate empathy and compassion in daily interactions. Practice understanding and sharing others’ feelings and be willing to offer help and support. These traits enhance social connections and promote positive interactions.
Thought
Social health is a vital aspect of overall well-being. It involves building and maintaining positive relationships, effective communication, strong social support networks, community engagement, adaptability, empathy, and compassion. The benefits of social health extend to improved mental and physical health, increased longevity, better coping mechanisms, enhanced self-esteem and confidence, a greater sense of belonging, and reduced risk of isolation. By nurturing relationships, improving communication skills, joining social groups, volunteering, seeking support, and practicing empathy, individuals can enhance their social health and overall quality of life.
5. Spiritual Health
Spiritual health involves a sense of purpose and meaning in life. It can be achieved through:
- Belief Systems: Following religious or philosophical beliefs.
- Purpose and Values: Understanding one’s purpose and adhering to personal values.
- Meditation and Reflection: Practicing mindfulness and self-reflection.
Intro to Spiritual Health
Spiritual health involves a sense of connection to something greater than oneself and encompasses a search for meaning in life. It is not limited to religious beliefs but includes a wide range of experiences and practices that enhance one’s inner life and provide a sense of purpose. Spiritual health is an essential component of overall well-being, influencing mental, emotional, and physical health.
Key Features of Spiritual Health
a. Sense of Purpose and Meaning
A fundamental aspect of spiritual health is the pursuit of purpose and meaning in life. This can be achieved through various avenues such as religion, philosophy, personal reflection, or connection with nature. Having a clear sense of purpose can provide direction and motivation in life.
b. Connection and Belonging
Spiritual health often involves feeling connected to others, whether through a religious community, family, friends, or nature. This sense of belonging fosters emotional support, compassion, and empathy, which are crucial for mental and emotional well-being.
c. Inner Peace and Calm
Achieving a state of inner peace and calm is a significant feature of spiritual health. Practices such as meditation, prayer, mindfulness, and yoga can help individuals attain a tranquil state of mind, reducing stress and anxiety.
d. Values and Morals
Spiritual health includes the development and adherence to a set of values and morals. These principles guide behavior, decision-making, and interactions with others, fostering a sense of integrity and ethical living.

e. Personal Growth and Self-Reflection
Engaging in self-reflection and striving for personal growth are key components of spiritual health. This involves examining one’s beliefs, values, and behaviors, and making conscious efforts to improve and evolve as an individual.
f. Resilience and Hope
Spiritual health can enhance resilience and the ability to cope with life’s challenges. It provides a source of hope and strength during difficult times, enabling individuals to persevere and find meaning even in adversity.
Benefits of Spiritual Health
a. Improved Mental Health
Spiritual health is closely linked to mental well-being. Practices that enhance spiritual health, such as meditation and mindfulness, have been shown to reduce symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. A strong sense of purpose and belonging can also improve overall mental health and emotional resilience.
b. Enhanced Physical Health
There is growing evidence that spiritual health positively impacts physical health. Individuals with strong spiritual health often engage in healthier lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and avoiding harmful behaviors. Additionally, the stress-reducing benefits of spiritual practices can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as hypertension and cardiovascular conditions.
c. Greater Life Satisfaction
A strong sense of purpose, inner peace, and connection with others contribute to greater life satisfaction. Individuals with good spiritual health often report higher levels of happiness, contentment, and fulfillment in their lives.

d. Better Coping Mechanisms
Spiritual health provides effective coping mechanisms for dealing with life’s challenges and stressors. Practices like prayer, meditation, and reflection offer comfort and support during tough times, fostering resilience and the ability to find meaning in adversity.
e. Enhanced Relationships
Spiritual health promotes compassion, empathy, and understanding, which enhance interpersonal relationships. A strong sense of connection and belonging can lead to more meaningful and supportive relationships with family, friends, and the broader community.
f. Increased Empathy and Compassion
Individuals with strong spiritual health often exhibit higher levels of empathy and compassion. These qualities foster positive interactions and relationships, contributing to a more supportive and harmonious community.
g. Personal Growth and Development
Engaging in spiritual practices encourages personal growth and self-improvement. It involves continuous self-reflection, learning, and the pursuit of higher values and principles, leading to a more fulfilling and enriched life.
Practical Tips for Enhancing Spiritual Health
a. Practice Mindfulness and Meditation
Incorporating mindfulness and meditation into daily routines can significantly enhance spiritual health. These practices promote inner peace, self-awareness, and a deeper connection with the present moment.
b. Engage in Self-Reflection
Regular self-reflection helps individuals understand their beliefs, values, and purpose. Journaling, contemplative walks, and quiet time for introspection are effective ways to engage in self-reflection.
c. Connect with Nature
Spending time in nature can foster a sense of connection and awe. Activities like hiking, gardening, or simply sitting in a park can enhance spiritual well-being by providing a peaceful and reflective environment.
d. Participate in a Community
Being part of a community, whether religious or secular, provides a sense of belonging and support. Engaging in group activities, volunteering, or attending gatherings can strengthen spiritual health.

e. Read Inspirational and Spiritual Texts
Reading books, articles, or scriptures that inspire and challenge one’s beliefs can provide new perspectives and deepen spiritual understanding. Engaging with diverse viewpoints can also enhance personal growth.
f. Practice Gratitude
Cultivating an attitude of gratitude can significantly enhance spiritual health. Regularly reflecting on and appreciating the positive aspects of life fosters a sense of contentment and connectedness.
g. Develop a Personal Spiritual Practice
Creating a personal spiritual practice tailored to individual beliefs and preferences can enhance spiritual health. This could include daily prayer, meditation, yoga, or any activity that fosters a sense of connection and purpose.
Thoughts
Spiritual health is a vital aspect of overall well-being, influencing mental, emotional, and physical health. By cultivating a sense of purpose, fostering connections, achieving inner peace, adhering to values, and engaging in self-reflection, individuals can enhance their spiritual health. The benefits of spiritual health are far-reaching, contributing to improved mental and physical health, greater life satisfaction, better coping mechanisms, enhanced relationships, and continuous personal growth. Incorporating practical tips such as mindfulness, self-reflection, nature connection, community participation, reading, gratitude, and personal spiritual practices can help individuals achieve and maintain good spiritual health.
6. Intellectual Health
Intellectual health encourages engaging in creative and stimulating mental activities. It includes:
- Lifelong Learning: Continuously seeking knowledge and learning new skills.
- Critical Thinking: Analyzing and evaluating information effectively.
- Creativity: Engaging in creative activities that stimulate the mind.
Intro to Intellectual Health
Intellectual health refers to the cognitive aspects of well-being, encompassing activities and pursuits that stimulate mental capacities and creativity. It involves the continuous pursuit of knowledge, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills, fostering an open mind to new ideas and experiences. Intellectual health is crucial for personal development and lifelong learning, impacting overall quality of life and well-being.
Key Features of Intellectual Health
a. Continuous Learning
A significant aspect of intellectual health is the pursuit of continuous learning. This can include formal education, self-study, reading, and engaging in intellectually stimulating activities. Continuous learning helps keep the mind active and engaged, promoting mental acuity and cognitive resilience.
b. Curiosity and Open-Mindedness
Intellectual health involves maintaining a sense of curiosity and open-mindedness towards new ideas, cultures, and perspectives. This willingness to explore and understand different viewpoints enhances critical thinking and adaptability, essential skills in an ever-changing world.
c. Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Developing strong critical thinking and problem-solving skills is a core component of intellectual health. These skills enable individuals to analyze situations, make informed decisions, and approach challenges with a logical and strategic mindset.

d. Creativity and Innovation
Encouraging creativity and innovation is vital for intellectual health. Engaging in creative activities such as writing, art, music, or any form of expression stimulates the brain and fosters innovative thinking. This not only enhances intellectual capabilities but also contributes to emotional and psychological well-being.
e. Engagement in Intellectual and Cultural Activities
Participating in intellectual and cultural activities, such as attending lectures, museums, theater performances, and engaging in debates or discussions, enriches intellectual health. These activities provide opportunities to expand knowledge, gain new insights, and connect with like-minded individuals.
f. Time Management and Organizational Skills
Effective time management and organizational skills are crucial for maintaining intellectual health. These skills help individuals prioritize tasks, manage responsibilities efficiently, and create a structured environment conducive to learning and intellectual growth.
Benefits of Intellectual Health
a. Enhanced Cognitive Function
Maintaining intellectual health has significant benefits for cognitive function. Continuous learning and mental stimulation help improve memory, attention, and reasoning abilities. Engaging in intellectually challenging activities has been shown to reduce the risk of cognitive decline and dementia in older adults.
b. Improved Problem-Solving Abilities
Developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills enhances an individual’s ability to navigate complex situations and make sound decisions. This leads to greater confidence and competence in both personal and professional settings.
c. Greater Creativity and Innovation
Fostering creativity and innovation through intellectual pursuits leads to the development of new ideas and solutions. This can be particularly beneficial in professional environments where innovative thinking is valued and rewarded.
d. Increased Knowledge and Understanding
Continuous learning and exposure to new information and perspectives broaden an individual’s knowledge base and understanding of the world. This can lead to greater empathy, cultural awareness, and the ability to engage in meaningful conversations on a variety of topics.
e. Enhanced Quality of Life
Intellectual health contributes to an overall sense of fulfillment and satisfaction. Engaging in activities that stimulate the mind and foster personal growth leads to a richer, more rewarding life experience.
f. Social Connections and Networking
Participating in intellectual and cultural activities provides opportunities to connect with others who share similar interests. Building these social connections can lead to valuable networking opportunities and a sense of community and belonging.

g. Better Mental Health
Maintaining intellectual health has positive effects on mental health. Engaging in intellectually stimulating activities can reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. It promotes a sense of purpose and achievement, which are important for overall mental well-being.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Intellectual Health
a. Pursue Lifelong Learning
Embrace the concept of lifelong learning by continually seeking new knowledge and experiences. Take courses, attend workshops, read books, and explore topics of interest to keep the mind active and engaged.
b. Challenge Yourself
Engage in activities that challenge your intellectual abilities. Solve puzzles, play strategy games, learn a new language, or take up a new hobby that requires mental effort and concentration.
c. Stay Curious
Cultivate a sense of curiosity and open-mindedness. Ask questions, explore new ideas, and be willing to step out of your comfort zone to gain new perspectives and insights.
d. Engage in Creative Activities
Incorporate creative activities into your routine. Whether it’s writing, painting, playing an instrument, or any other form of artistic expression, these activities stimulate the brain and foster intellectual growth.
e. Manage Time Effectively
Develop good time management and organizational skills. Create a structured schedule that allows time for intellectual pursuits and ensures a balanced approach to work, study, and leisure activities.
f. Connect with Others
Participate in intellectual and cultural events and engage in discussions with others. Join clubs, attend lectures, and be part of communities that value intellectual growth and exploration.
g. Take Care of Physical Health
Physical health and intellectual health are interconnected. Ensure you get enough sleep, exercise regularly, and maintain a balanced diet. A healthy body supports a healthy mind.
Thoughts
Intellectual health is an essential component of overall well-being, contributing to cognitive function, creativity, problem-solving abilities, and personal growth. By engaging in continuous learning, fostering curiosity, and participating in intellectually stimulating activities, individuals can enhance their intellectual health and enjoy a more fulfilling and enriched life.
7. Vocational Health
Vocational health refers to finding fulfillment and satisfaction in one’s work. It involves:
- Career Satisfaction: Finding joy and purpose in one’s job.
- Work-Life Balance: Balancing work responsibilities with personal life.
- Professional Development: Pursuing growth and development in one’s career.
Intro to Vocational Health
Vocational health refers to the physical and mental well-being of an individual in relation to their work environment and occupational activities. It encompasses a range of factors, including job satisfaction, work-life balance, safety, ergonomics, and professional development. Vocational health is essential for maintaining productivity, job satisfaction, and overall well-being.
Key Features of Vocational Health
a. Job Satisfaction
Job satisfaction is a crucial component of vocational health. It refers to the contentment and fulfillment individuals feel regarding their work. Factors contributing to job satisfaction include meaningful work, recognition, fair compensation, and a positive work environment.
b. Work-Life Balance
Maintaining a healthy balance between work responsibilities and personal life is essential for vocational health. It involves managing time effectively to ensure that work does not encroach excessively on personal time, leading to stress and burnout.
c. Workplace Safety
Ensuring a safe work environment is a fundamental aspect of vocational health. This includes implementing safety protocols, providing proper training, and addressing potential hazards to prevent accidents and injuries.
d. Ergonomics
Ergonomics focuses on designing workspaces and tasks to fit the physical capabilities of employees. Proper ergonomic practices reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and improve comfort and productivity.
e. Professional Development
Opportunities for professional growth and development are vital for vocational health. Continuous learning, skill development, and career advancement contribute to job satisfaction and motivation.
f. Stress Management
Effective stress management strategies are essential for maintaining vocational health. This includes providing resources for mental health support, promoting a positive work culture, and encouraging healthy coping mechanisms.
Benefits of Vocational Health
a. Increased Productivity
Employees who are satisfied with their jobs and work in a healthy environment are more productive. High vocational health reduces absenteeism, enhances focus, and improves the quality of work.
b. Enhanced Job Satisfaction
A positive work environment and opportunities for growth lead to higher job satisfaction. Satisfied employees are more engaged, motivated, and loyal to their organization.
c. Reduced Health Risks
Implementing safety measures and ergonomic practices reduces the risk of workplace injuries and health issues. This leads to fewer sick days and lower healthcare costs for both employees and employers.
d. Improved Mental Health
A supportive work environment that promotes work-life balance and stress management improves mental health. Reduced stress and anxiety contribute to overall well-being and job performance.
e. Better Employee Retention
Organizations that prioritize vocational health are more likely to retain talented employees. High retention rates reduce recruitment and training costs and maintain organizational stability.
f. Enhanced Professional Growth
Opportunities for professional development enhance employees’ skills and career prospects. This leads to a more skilled and adaptable workforce, benefiting both individuals and the organization.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Vocational Health
a. Promote a Positive Work Culture
Fostering a positive work culture involves creating an environment of respect, recognition, and support. Encourage open communication and collaboration among employees.
b. Encourage Work-Life Balance
Implement policies that support work-life balance, such as flexible working hours, remote work options, and adequate vacation time. Encourage employees to take breaks and manage their workload effectively.

c. Prioritize Workplace Safety
Regularly assess and address potential safety hazards. Provide comprehensive safety training and ensure that all safety protocols are followed. Invest in ergonomic equipment and practices to prevent injuries.
d. Support Professional Development
Offer opportunities for continuous learning and career advancement. Provide access to training programs, workshops, and mentorship to help employees develop their skills and achieve their career goals.
e. Provide Mental Health Resources
Promote mental health awareness and provide resources for support. This includes access to counseling services, stress management programs, and initiatives that promote a healthy work-life balance.
f. Foster Open Communication
Encourage open and transparent communication between employees and management. Regular feedback and constructive discussions help address concerns and improve job satisfaction.
Thoughts
Vocational health is a critical aspect of overall well-being that encompasses job satisfaction, work-life balance, workplace safety, ergonomics, professional development, and stress management. Prioritizing vocational health benefits both employees and organizations by increasing productivity, enhancing job satisfaction, reducing health risks, improving mental health, and fostering professional growth. By implementing strategies to promote vocational health, organizations can create a supportive and thriving work environment.
8. Financial Health
Financial health is about managing one’s financial resources effectively. It includes:
- Budgeting: Planning and controlling how money is spent.
- Saving: Setting aside money for future needs.
- Debt Management: Managing and reducing debt responsibly.
Intro to Financial Health
Financial health refers to the state of an individual’s or organization’s financial situation. It includes the ability to meet current and future financial obligations, feel secure in one’s financial future, and make choices that allow for a satisfying life. Financial health encompasses various aspects such as income, expenses, savings, investments, debt, and credit management.
Key Features of Financial Health
a. Stable Income
A stable and sufficient income is the foundation of financial health. It ensures that basic needs are met, including housing, food, healthcare, and other essentials. Stable income provides a sense of security and allows for planning and achieving financial goals.
b. Budgeting and Expense Management
Effective budgeting and expense management involve tracking income and expenditures, prioritizing spending, and avoiding unnecessary expenses. Creating and adhering to a budget helps in controlling spending, reducing debt, and saving for future needs.
c. Savings and Emergency Fund
Having adequate savings and an emergency fund is crucial for financial stability. Savings can be used for planned expenses, investments, and unexpected emergencies, such as medical expenses or job loss. An emergency fund typically covers 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses.

d. Investment and Wealth Building
Investing in various assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and retirement accounts helps build wealth over time. Diversified investments provide opportunities for growth and financial security, ensuring long-term financial health.
e. Debt Management
Managing debt effectively involves minimizing high-interest debts, making timely payments, and avoiding excessive borrowing. Good debt management improves credit scores and reduces financial stress.
f. Credit Score Maintenance
Maintaining a good credit score is essential for financial health. It impacts the ability to obtain loans, credit cards, and favorable interest rates. Regularly monitoring and improving one’s credit score through responsible financial behavior is vital.
g. Financial Planning and Goal Setting
Setting clear financial goals and creating a financial plan to achieve them is a key feature of financial health. This includes short-term goals like saving for a vacation and long-term goals like buying a house or retirement planning.
Benefits of Financial Health
a. Reduced Stress and Anxiety
Good financial health reduces stress and anxiety associated with money problems. Knowing that you can meet your financial obligations and handle emergencies provides peace of mind and improves overall well-being.
b. Improved Quality of Life
Financial health allows for a better quality of life by enabling individuals to afford necessities and luxuries. It provides the freedom to pursue interests, hobbies, and experiences that contribute to personal fulfillment.
c. Increased Financial Security
Having a stable financial foundation and adequate savings ensures financial security. It protects against economic downturns, job loss, and unexpected expenses, providing a safety net for the future.
d. Ability to Achieve Financial Goals
Financial health facilitates the achievement of both short-term and long-term financial goals. Whether it’s buying a home, funding education, starting a business, or retiring comfortably, financial health makes these goals attainable.
e. Better Credit Opportunities
Maintaining good financial health improves credit scores, leading to better credit opportunities. It allows individuals to access loans and credit cards with favorable terms, lower interest rates, and better rewards programs.
f. Opportunity for Wealth Accumulation
Good financial health enables individuals to invest and grow their wealth. It opens up opportunities for higher returns on investments, real estate, and other wealth-building activities, leading to financial independence.
g. Enhanced Financial Literacy
Focusing on financial health increases financial literacy. Understanding financial concepts and managing money effectively leads to informed decision-making and better financial outcomes.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Financial Health
a. Create and Stick to a Budget
Develop a detailed budget that outlines income, expenses, and savings goals. Track spending to ensure adherence to the budget and make adjustments as needed.
b. Build an Emergency Fund
Save at least 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses in an emergency fund. This provides a financial cushion in case of unexpected events.
c. Reduce and Manage Debt
Pay off high-interest debts first and avoid accumulating new debts. Use strategies like debt consolidation or refinancing to manage and reduce debt effectively.
d. Save and Invest Regularly
Set up automatic transfers to savings and investment accounts. Regular contributions, even in small amounts, help in building wealth over time.
e. Monitor Credit Score
Regularly check your credit report and score. Address any discrepancies and take steps to improve your credit score, such as making timely payments and reducing debt.
f. Plan for Retirement
Start saving for retirement early and take advantage of employer-sponsored retirement plans and individual retirement accounts (IRAs). Invest in a diversified portfolio to grow your retirement savings.
g. Seek Professional Advice
Consult with financial advisors or planners for personalized advice and strategies. Professional guidance can help in making informed decisions and achieving financial goals.
Thoughts
Financial health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, impacting every area of life. By maintaining stable income, managing expenses, building savings and investments, managing debt, maintaining good credit, and setting financial goals, individuals can achieve financial stability and security. The benefits of financial health extend beyond financial security, contributing to reduced stress, improved quality of life, and the ability to achieve personal and financial goals. Focusing on financial health leads to greater financial literacy and independence, paving the way for a secure and prosperous future.
9. Environmental Health
Environmental health focuses on the interaction between people and their environment. It involves:
- Living Conditions: Ensuring a safe and healthy living environment.
- Sustainable Practices: Adopting eco-friendly habits to protect the environment.
- Public Health: Understanding how environmental factors affect overall health.
Intro to Environmental Health
Environmental health is the branch of public health that focuses on the interrelationships between people and their environment, promotes human health and well-being, and fosters healthy and safe communities. Environmental health involves assessing and controlling physical, chemical, and biological factors that can potentially affect health.
Key Features of Environmental Health
a. Air Quality
Air quality is a critical aspect of environmental health. Poor air quality, caused by pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and carbon monoxide, can lead to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues. Monitoring and improving air quality is essential for reducing health risks.
b. Water Quality
Access to clean and safe drinking water is fundamental to health. Contaminated water can cause a range of diseases, including cholera, dysentery, and other gastrointestinal illnesses. Ensuring water safety through proper treatment and sanitation practices is a core component of environmental health.
c. Waste Management
Proper waste management, including the disposal of household waste, industrial waste, and hazardous materials, is crucial for preventing pollution and protecting public health. Effective waste management practices reduce the risk of environmental contamination and the spread of diseases.
d. Food Safety
Environmental health includes ensuring the safety of the food supply. This involves regulating food production, processing, and distribution to prevent foodborne illnesses caused by contaminants such as bacteria, viruses, pesticides, and heavy metals.
e. Chemical Safety
Chemical safety involves managing and controlling the use of chemicals to prevent exposure to toxic substances. This includes monitoring industrial chemicals, pesticides, and household products to minimize health risks associated with chemical exposure.
f. Climate Change
Climate change has significant impacts on environmental health. Changes in climate can affect air and water quality, food security, and the prevalence of vector-borne diseases. Addressing climate change through mitigation and adaptation strategies is essential for protecting health.
g. Housing and Urban Development
Safe and healthy housing conditions are a vital aspect of environmental health. Poor housing conditions, such as inadequate ventilation, overcrowding, and exposure to hazardous materials, can lead to various health problems. Urban planning and development that prioritize health and safety contribute to better living environments.
Benefits of Environmental Health
a. Reduced Disease Burden
Effective environmental health measures significantly reduce the burden of diseases. By controlling environmental hazards and promoting clean air, water, and safe food, the incidence of infectious and non-communicable diseases decreases, leading to improved overall health outcomes.
b. Enhanced Quality of Life
Improving environmental health enhances the quality of life by creating healthier living and working conditions. Clean air, safe water, and well-managed waste systems contribute to a more pleasant and healthy environment, fostering well-being and comfort.
c. Increased Life Expectancy
Populations living in environments with high-quality air and water and effective waste management systems generally experience increased life expectancy. Reducing exposure to environmental hazards lowers the risk of chronic diseases and premature death.
d. Economic Benefits
Investing in environmental health can lead to significant economic benefits. Reducing the incidence of disease lowers healthcare costs and increases productivity. Moreover, a healthy environment can attract tourism and promote economic development.
e. Improved Mental Health
A clean and safe environment positively impacts mental health. Access to green spaces, clean air, and safe living conditions reduces stress and promotes mental well-being. Environmental health initiatives that improve urban environments can contribute to lower levels of anxiety and depression.
f. Resilience to Climate Change
Environmental health practices that address climate change contribute to community resilience. Mitigation and adaptation strategies help communities cope with the impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events, ensuring sustained health and well-being.
4. Practical Tips for Maintaining Environmental Health
a. Reduce Air Pollution
Individuals can contribute to improving air quality by using public transportation, carpooling, reducing energy consumption, and supporting policies that limit industrial emissions. Planting trees and supporting green spaces also help improve air quality.
b. Ensure Water Safety
Ensuring access to clean drinking water involves using water filters, properly disposing of hazardous materials, and supporting infrastructure projects that provide safe water. Communities should advocate for regulations that protect water sources from contamination.
c. Practice Responsible Waste Management
Reduce, reuse, and recycle to minimize waste. Properly dispose of hazardous materials, compost organic waste, and support policies that promote sustainable waste management practices. Participating in community clean-up initiatives can also help maintain a clean environment.
d. Promote Food Safety
Individuals can promote food safety by washing hands and surfaces frequently, cooking food to the right temperatures, and storing food properly. Supporting local and organic food producers who follow safe and sustainable practices also contributes to food safety.
e. Use Chemicals Safely
Reduce the use of harmful chemicals in households by choosing non-toxic, biodegradable products. Properly store and dispose of chemicals, and support regulations that limit the use of hazardous substances in industry and agriculture.
f. Address Climate Change
Combat climate change by reducing carbon footprints through energy conservation, using renewable energy sources, and supporting policies that promote sustainability. Advocate for climate action at local, national, and global levels to protect environmental health.
g. Advocate for Safe Housing
Promote safe and healthy housing by ensuring proper ventilation, reducing exposure to indoor pollutants, and supporting housing policies that prioritize health and safety. Engage in community efforts to improve housing conditions, especially in underserved areas.
Thoughts
Environmental health is a crucial aspect of public health that requires collective effort from individuals, communities, and governments. By addressing key features such as air and water quality, waste management, food safety, chemical safety, climate change, and housing, we can create healthier environments. The benefits of maintaining environmental health are profound, including reduced disease burden, enhanced quality of life, increased life expectancy, economic benefits, improved mental health, and resilience to climate change. Practical measures and advocacy are essential to ensuring a sustainable and healthy environment for current and future generations.
The Interconnectedness of Health Types
While each type of health is distinct, they are all interconnected. Improving one aspect often positively impacts others. For instance, regular physical activity can enhance mental health, while strong social connections can improve emotional health.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and nurturing all types of health is essential for achieving overall well-being. By paying attention to physical, mental, emotional, social, spiritual, intellectual, vocational, financial, and environmental health, individuals can lead balanced and fulfilling lives. Holistic health is not a destination but a continuous journey of growth and improvement.









[…] You May Also Like Reading The 8 Best Steps To Healthy Living […]
[…] You May Also Like Reading The 8 Best Steps To Healthy Living […]